这篇文章主要介绍了postgreSQL中的row_number() 与distinct用法说明,具有很好的参考价值,希望对大家有所帮助。一起跟随小编过来看看吧。
我就废话不多说了,大家还是直接看代码吧~
select count(s.*)
from (
select *, row_number() over (partition by fee_date order by fee_date) as gr
from new_order where news_id='novel' and order_status='2'
) s
where s.gr = 1
SELECT count(DISTINCT fee_date) as dis from new_order where news_id='novel' and order_status='2'
这两个SQL执行所得到的数据是一样的!
工具:postgreSQL
1.我们要清楚,sql的执行顺序:
from语句->where语句->group by语句->having语句->order by语句->select 语句
2.row_number()分析函数
说明:返回结果集分区内行的序列号,每个分区的第一行从 1 开始。
语法:ROW_NUMBER () OVER ([ <partition_by_clause>]<order_by_clause> )
备注:ORDERBY 子句可确定在特定分区中为行分配唯一 ROW_NUMBER 的顺序。
参数:<partition_by_clause> :将FROM 子句生成的结果集划入应用了 ROW_NUMBER 函数的分区。
<order_by_clause>:确定将 ROW_NUMBER 值分配给分区中行的顺序。
返回类型:bigint 。
row_number()从1开始,为每一条分组记录返回一个数字
1select *, row_number() over (order by fee_date) from new_order
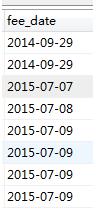
先把 fee_date 升序排列,再为升序以后的每条记录返回一个序号
1select *, row_number() over (partition by fee_date order by fee_date) as gr from new_order
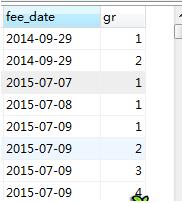
表示根据fee_date分组,在分组内部根据 fee_date排序,而此函数计算的值就表示每组内部排序后的顺序编号(组内连续的唯一的)
2.distinct
语法:
1SELECT DISTINCT 列名称 FROM 表名称
distinct这个关键字用来过滤掉多余的重复记录只保留一条
1select DISTINCT fee_date from new_order
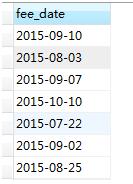
1select DISTINCT fee_date,order_status from new_order
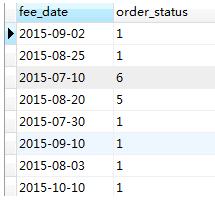
从结果可以看出,是根据“fee_date+order_status”来去重复数据的,distinct同时作用在了fee_date和order_status上
1SELECT count(DISTINCT fee_date) as dis from new_order where news_id='novel' and order_status='2'

1select id,distinct fee_date from new_order ; –会提示错误,因为distinct必须放在开头
distinct语句中select显示的字段只能是distinct指定的字段,其他字段是不可能出现的
补充:PostgreSQL ROW_NUMBER() OVER()
我就废话不多说了,大家还是直接看代码吧~
SELECT
*
FROM
(
SELECT
tt.s_ci s_ci,
sm.ci,
-- getdistance (
-- tt.longitude,
-- tt.latitude,
-- sm.longitude,
-- sm.latitude
-- ) distance,
ROW_NUMBER () OVER (
PARTITION BY tt.s_ci
ORDER BY
getdistance (
tt.longitude,
tt.latitude,
sm.longitude,
sm.latitude
)
) rn
FROM
sm_cl_location sm
INNER JOIN (
SELECT
s_ci,
longitude,
latitude,
n3_pci,
n3_earfcn
FROM
plan_ott_data
WHERE
1 = 1
AND (
s_ci = '460-00-1012286-2'
OR s_ci = '460-00-25514-130'
)
AND rpt_time BETWEEN '2018-04-30'
AND '2018-05-29'
) tt ON sm.pci = tt.n3_pci
AND sm.hannel_number = tt.n3_earfcn
) T
WHERE
T .rn BETWEEN 1 and 3
语法:
1ROW_NUMBER() OVER( [ PRITITION BY col1] ORDER BY col2[ DESC ] )
解释:
ROW_NUMBER()为返回的记录定义个行编号, PARTITION BY col1 是根据col1分组,ORDER BY col2[ DESC ]是根据col2进行排序。
举例:
postgres=# create table student(id serial,name character varying,course character varying,score integer);
CREATE TABLE
postgres=#
postgres=# d student
Table "public.student"
Column | Type | Modifiers
--------+-------------------+----------------------------------------------
id | integer | not null default nextval('student_id_seq'::regclass)
name | character varying |
course | character varying |
score | integer |
insert into student (name,course,score) values('周润发','语文',89);
insert into student (name,course,score) values('周润发','数学',99);
insert into student (name,course,score) values('周润发','外语',67);
insert into student (name,course,score) values('周润发','物理',77);
insert into student (name,course,score) values('周润发','化学',87);
insert into student (name,course,score) values('周星驰','语文',91);
insert into student (name,course,score) values('周星驰','数学',81);
insert into student (name,course,score) values('周星驰','外语',88);
insert into student (name,course,score) values('周星驰','物理',68);
insert into student (name,course,score) values('周星驰','化学',83);
insert into student (name,course,score) values('黎明','语文',85);
insert into student (name,course,score) values('黎明','数学',65);
insert into student (name,course,score) values('黎明','外语',95);
insert into student (name,course,score) values('黎明','物理',90);
insert into student (name,course,score) values('黎明','化学',78);
1. 根据分数排序
postgres=# select *,row_number() over(order by score desc)rn from student;
id | name | course | score | rn
----+--------+--------+-------+----
2 | 周润发 | 数学 | 99 | 1
13 | 黎明 | 外语 | 95 | 2
6 | 周星驰 | 语文 | 91 | 3
14 | 黎明 | 物理 | 90 | 4
1 | 周润发 | 语文 | 89 | 5
8 | 周星驰 | 外语 | 88 | 6
5 | 周润发 | 化学 | 87 | 7
11 | 黎明 | 语文 | 85 | 8
10 | 周星驰 | 化学 | 83 | 9
7 | 周星驰 | 数学 | 81 | 10
15 | 黎明 | 化学 | 78 | 11
4 | 周润发 | 物理 | 77 | 12
9 | 周星驰 | 物理 | 68 | 13
3 | 周润发 | 外语 | 67 | 14
12 | 黎明 | 数学 | 65 | 15
(15 rows)
rn是给我们的一个排序。
2. 根据科目分组,按分数排序
postgres=# select *,row_number() over(partition by course order by score desc)rn from student;
id | name | course | score | rn
----+--------+--------+-------+----
5 | 周润发 | 化学 | 87 | 1
10 | 周星驰 | 化学 | 83 | 2
15 | 黎明 | 化学 | 78 | 3
13 | 黎明 | 外语 | 95 | 1
8 | 周星驰 | 外语 | 88 | 2
3 | 周润发 | 外语 | 67 | 3
2 | 周润发 | 数学 | 99 | 1
7 | 周星驰 | 数学 | 81 | 2
12 | 黎明 | 数学 | 65 | 3
14 | 黎明 | 物理 | 90 | 1
4 | 周润发 | 物理 | 77 | 2
9 | 周星驰 | 物理 | 68 | 3
6 | 周星驰 | 语文 | 91 | 1
1 | 周润发 | 语文 | 89 | 2
11 | 黎明 | 语文 | 85 | 3
(15 rows)
3. 获取每个科目的最高分
postgres=# select * from(select *,row_number() over(partition by course order by score desc)rn from student)t where rn=1;
id | name | course | score | rn
----+--------+--------+-------+----
5 | 周润发 | 化学 | 87 | 1
13 | 黎明 | 外语 | 95 | 1
2 | 周润发 | 数学 | 99 | 1
14 | 黎明 | 物理 | 90 | 1
6 | 周星驰 | 语文 | 91 | 1
(5 rows)
4. 每个科目的最低分也是一样的
postgres=# select * from(select *,row_number() over(partition by course order by score)rn from student)t where rn=1;
id | name | course | score | rn
----+--------+--------+-------+----
15 | 黎明 | 化学 | 78 | 1
3 | 周润发 | 外语 | 67 | 1
12 | 黎明 | 数学 | 65 | 1
9 | 周星驰 | 物理 | 68 | 1
11 | 黎明 | 语文 | 85 | 1
(5 rows)
只要在根据科目排序的时候按低到高顺序排列就好了。
文章来源:脚本之家
来源地址:https://www.jb51.net/article/204797.htm