使用背景
最近在使用PostgreSQL的时候,在执行一些数据库事务的时候,先后出现了statement timetout 和idle-in-transaction timeout的问题,导致数据库操作失败。
经研究查找,PostgreSQL有关于SQL语句执行超时和事务执行超时的相关配置,而默认超时时间是10000毫秒,即10秒钟的时间,这样会导致执行时间稍长的任务执行失败。可以通过修改PostgreSQL服务器配置文件的方式修改默认配置。
参数说明
statement_timeout
statement_timeout 在 postgresql 被用来控制语句执行时长,单位是ms。
$ vi postgresql.conf
#statement_timeout = 0 # in milliseconds, 0 is disabled
默认是0,表示语句可以一直执行下去。
如果设置为10000,那就意味着语句最多可以执行 10000ms = 10s。
建议设置为0,禁用该参数。
1idle_in_transaction_session_timeout
PostgreSQL 9.6版本开始支持自动查杀超过指定时间的 idle in transaction 空闲事务连接,用于清理应用代码中忘记关闭已开启的事务,或者系统中存在僵死进程等。
idle_in_transaction_session_timeout 在 postgresql 被用来控制事务执行时长,单位是ms。
$ vi postgresql.conf #idle_in_transaction_session_timeout = 0 # in milliseconds, 0 is disabled
默认是0,表示语句可以一直执行下去。超时会报 FATAL: terminating connection due to idle-in-transaction timeout。
修改方法
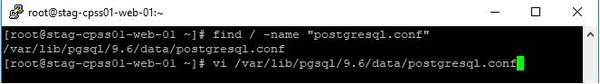
查找配置
通过命令查找到postgresql配置文件的位置,用vi进行编辑。
1
2find / -name "postgresql.conf"vi /var/lib/pgsql/9.6/data/postgresql.conf
修改参数
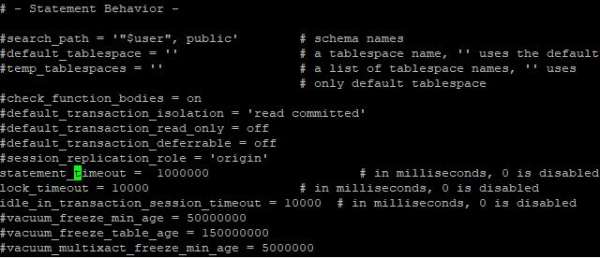
进入vi编辑界面,可以通过vi查找命令定位到相关参数,修改成合适的时间,保存退出。
:/statement_timeout
重启配置
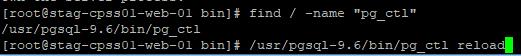
通过以下命令,查找pg_ctl的位置,然后执行 pg_ctl reload重新加载配置。
1
2find / -name "pg_ctl"/usr/pgsql-9.6/bin/pg_ctl reload
PG_CTL用法
启动服务器
启动服务器:
1$ pg_ctl start
启动服务器的一个例子,等到服务器启动了才退出:
1$ pg_ctl -w start
服务器使用 5433 端口,而且不带 fsync 运行,使用:
1$ pg_ctl -o "-F -p 5433" start
停止服务器
1$ pg_ctl stop
使用 -m 选项停止服务器允许用户控制如何关闭后端。
重启服务器
这个命令几乎等于先停止服务器然后再启动它,只不过 pg_ctl 保存并重新使用上一次运行服务器的命令行参数。重启服务器的最简单的方法是:
1$ pg_ctl restart
重启服务器,等待其停止和重启:
1$ pg_ctl -w restart
使用 5433 端口重启并且重启后关闭 fsync :
1$ pg_ctl -o "-F -p 5433" restart
显示服务器状态
下面是来自 pg_ctl 的状态输出的例子:
$ pg_ctl statuspg_ctl: server is running (pid: 13718)
Command line was:
/usr/local/pgsql/bin/postgres '-D' '/usr/local/pgsql/data' '-p' '5433' '-B' '128'
这就是在 restart 模式中被调用的命令行。
补充:PostgreSQL 设置单条SQL的执行超时 - 防雪崩
背景
设置单条SQL的执行超时,防雪崩。
通常来说可以在SQL发起前设置事务级超时参数,SQL执行结束,重置。(如果SQL异常退出,会自动重置事务级参数)
例子
begin;
......
set local statement_time='100ms';
select count(*) from a; -- 这条SQL的执行时间超过100MS则主动退出,并回滚整个事务
set local statement_timeout to default;
......
end;
函数级超时例子 - statement_timeout不可用
例如这个QUERY,我们想让它100毫秒超时。
1select count(*) as cnt, id from a where id<$1 group by id;
将它写到函数中,在函数中设置超时
create or replace function f1(int) returns setof record as $$
declare
begin
set local statement_timeout='100ms';
return query select count(*) as cnt, id from a where id<$1 group by id;
end;
$$ language plpgsql strict ;
调用SQL改成这样
1select cnt,id from f1(1) as t(cnt int8, id int);
但是这么做实际上是没有效果的,原因是statement_timeout的设计之初是为交互性SQL设计的,在postgres.c中。
所以需要plpgsql超时,需要通过插件HOOK来实现。
https://www.postgresql.org/message-id/flat/200702201200.53535.xzilla%40users.sourceforge.net#200702201200.53535.xzilla@users.sourceforge.net
statement_timeout is measured across an entire interactive command, not
individual commands within a function; and the timeout that applies to
an interactive command is determined at its beginning. So the above
doesn't do what you think.
参数级别
1、实例级
修改
1postgresql.conf
2、库级
1alter database dbname set parameter=?;
3、用户级
1alter role rolname set parameter=?;
4、会话级
1set parameter=?;
5、事务级
begin;
set local parameter=?;
....
end;
6、函数级
1alter function fun_name() set parameter=?;
其他超时控制
1、空闲事务超时
1idle_in_transaction_session_timeout = 2h
2、锁等待超时
1lock_timeout = 1s
3、死锁检测超时间隔
1deadlock_timeout = 1s
文章来源:脚本之家
来源地址:https://www.jb51.net/article/204224.htm